75. The Spanish Savior of St. Louis
|
By Miguel Pérez
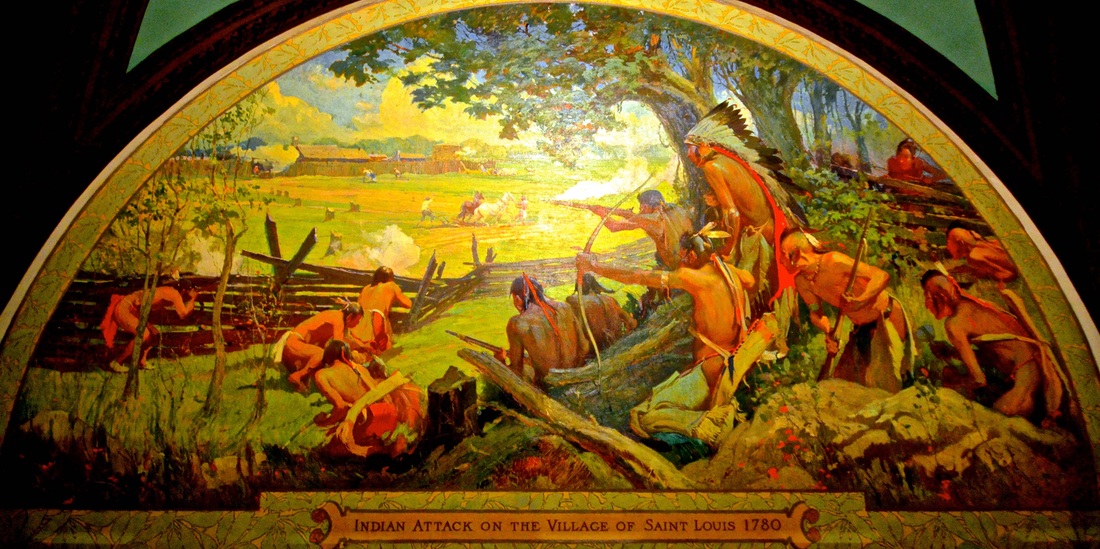
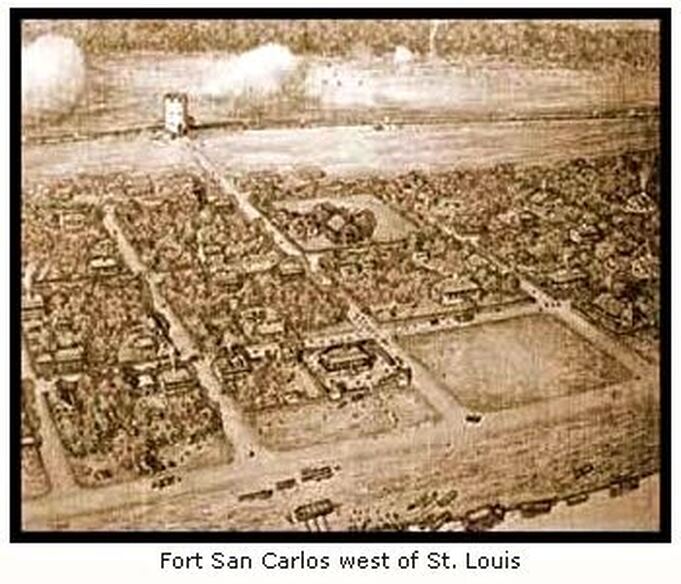
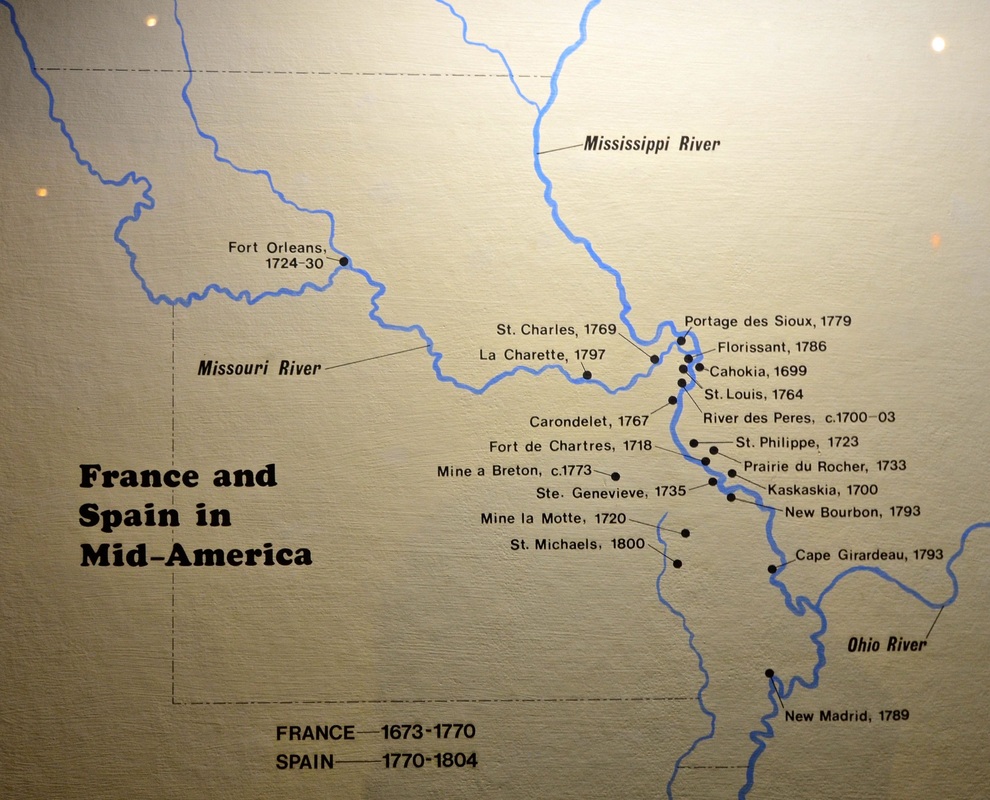
Jan. 6, 2015 -Somewhere beneath the Hilton Hotel and Ballpark Village — the fancy new complex built by the St. Louis Cardinals next to Busch Stadium in downtown St. Louis — lie the remains of an old Spanish fort that played a key role in defeating the British during the American Revolution. In fact, had it not been for Fort San Carlos, hastily built by Spanish troops and French Creole settlers to protect the small village of St. Louis in 1780, some historians believe American independence from Great Britain would not have been achieved. Yet only a small plaque remains to mark the place where such momentous events occurred. If you are not looking for it, you are probably going to miss it. But near the corner of South Broadway and Walnut Street, outside the Hilton's main entrance, the plaque explains the area's historical significance: "Near this spot stood Fort San Carlos erected in 1780. It was attacked May 28, 1780 by the British and Indians and successfully defended by the Spanish garrison under Captain Fernando de Leyba. This victory prevented Great Britain from gaining control of the Mississippi Valley in the later years of the American Revolutionary War." De Leyba also was the lieutenant governor of Spanish Louisiana, which had been ceded by France to Spain in 1763. Most of the town's 700 inhabitants were French Creoles. He had been sent to St. Louis in 1778 — by the governor of Louisiana, Bernardo de Galvez — to govern over what was then the administrative capital of northern Louisiana Territory and to collaborate with Americans, who were fighting for their independence from Britain. As the Great Hispanic American History Tour went through Pensacola, Florida, and Mobile, Alabama, a few months ago, we saw how Galvez covered "the Hispanic flank of the American Revolution" — along the Gulf Coast, east and west of the Mississippi River — and how Hispanic forces prevented the British from attacking the rear flank of George Washington's troops. And if you think their contributions have been unfairly buried in American history — as our tour reaches Missouri — you'll find that even more hidden is the story of the only Revolutionary War battle fought west of the Mississippi, where Spanish soldiers again stopped the British from flanking American troops. At the Battle of St. Louis — also known as the Battle of Fort San Carlos — Leyba led a small militia of fewer than 200 men — including some 30 Spanish soldiers — and held off a barrage of attacks from two dozen British and Canadian fur traders and more than 1,000 warriors from a half-dozen Indian tribes the traders had recruited to wage war on St. Louis. It was all part of a major British offensive, in the spring of 1780, to take control of the upper Mississippi and eventually attack the Colonies from the rear. Sitting on the western bank of the Mississippi, St. Louis was mostly a trading center before the war. But following orders from Galvez to assist the American Revolution, de Leyba worked in collaboration with American patriot George Rogers Clark, the leader of the Kentucky militia, even encouraging St. Louis merchants to supply Clark's troops with guns, clothing and other goods on credit. Yet when de Leyba learned of an imminent British-led attack on the village, Clark was involved in another skirmish at Cahokia, on the eastern side of the Mississippi, and Galvez, engaged in his own campaign against British outposts in the lower Mississippi Valley and along the Gulf Coast, sent word that St. Louis would have to defend itself without reinforcements. De Leyba hurriedly mounted a campaign to fortify the town, with funds raised from the villagers and from his own pocket. He wanted to build four stone towers on a hill and gain cannon supremacy over the area. But he only had time to finish one tower and a series of trenches — stretching along the town's southern and northern borders — before the May 28 attack. Nevertheless, although the villagers were greatly outnumbered, the five cannons mounted on the completed tower — and some 150 muskets in the trenches — caught the British by surprise and repelled a series of attacks that could have changed the course of American history. Apparently, area historians say, also working in St. Louis' favor was Britain's inability to get the Indians to form a single army and agree on a unified plan of attack. Instead, as if competing with one another, various tribes took turns attacking the fort in small raids, seemingly more concerned with proving their bravery to one another than with following British orders. Mind you, St. Louis suffered numerous casualties — 21 killed and dozens wounded or taken captive — especially from the villagers caught outside the fortified area during the first attack by several hundred Indians. "The certainty in which they were of finding the post without any fortification caused them to advance like madmen, with an unbelievable boldness and fury, making terrible cries and a terrible firing," de Leyba later reported in a letter to Galvez. "If it had not been for the rapidity with which I acted, together with all the people on the fortifications, it would have been the last day of St. Louis." After various raids had failed to penetrate the town's reinforcements, de Leyba reported to Galvez that the natives had brutally murdered some of their captives to try to anger the settlers and draw them out of the fort. And they almost succeeded! "Alas! My governor," de Leyba wrote to Galvez, "your paternal heart would have shed tears if you had been able to see with your own eyes a spectacle so emotional. It was an affliction and general consternation, to see these poor corpses cut into pieces, their entrails (pulled out), their limbs, heads, arms and legs scattered all over the field. What a horrible spectacle, mon general. In detailing this to you, I find myself very deeply grieved with great pain." When the town's militia sought to organize a sortie to pursue the attackers, it was de Leyba who resisted, ordering the townsfolk to stay in the fortified area until the attacking natives he called "barbarians animated by the English" finally gave up on St. Louis. The natives — Sioux, Chippewa, Menominee, Winnebago, Sauk and Fox — wiped out crops, livestock and farm homes and took captives as they retreated to the north, but their inability to conquer St. Louis effectively ended British efforts to take control of the Mississippi River during the war. De Leyba, who was already gravely ill, probably suffering from malaria, died only a month later. When the reports of his accomplishments reached Galvez and the king of Spain, they celebrated his leadership and heroism and promoted him posthumously to lieutenant colonel. Yet after de Leyba's death, instead of recognizing him for saving St. Louis from untold mayhem, some of his local critics, mostly anonymously, set out on a campaign to damage his reputation, claiming that he could have somehow prevented the Indian massacre outside the fort. Although these charges were given validity by some 19th-century historians, others have since recognized the huge role de Leyba played in saving St. Louis and — just like Galvez — defending the American frontier and winning the Revolutionary War. Fort San Carlos — named after the king of Spain — grew after de Leyba's death, until it was torn down in 1818 to make way for urban renewal in the growing city of St. Louis. Although local archeologists believe artifacts from Fort San Carlos could still be found under Busch Stadium, Ballpark Village and the Hilton, in downtown St. Louis — except for the plaque — you will find little trace of this precious history. The Great Hispanic American History Tour had to make another stop at the Missouri State Capitol in Jefferson City just to see Oscar Berninghaus' 1924 mural depicting the "Indian Attack on the Village of St. Louis" and get a better image of this Hispanic flank of the American Revolution. Next week, the Great Hispanic American History Tour goes to Charlottesville, Virginia, in search of a Spanish treasure in Thomas Jefferson's bookshelves. COPYRIGHT 2015 CREATORS.COM |
"House Of Thunder," is a great documentary! It is based on the book "The Battle of St. Louis, The Attack on Cahokia and The American Revolution in the West. Although no longer available online, this trailer is misleading. While the movie certainly credits the Spanish for saving St. Louis and probably the entire country, the trailer is edited in a way that the Spanish are not mentioned. Hidden Hispanic Heritage?
Downtown St. Louis:
The Gateway Arch:
Missouri State Capitol in Jefferson City:
Missouri State Museum in Jefferson City:
|
Please share this article with your friends on social media: